WISC Test Online: All You Need to Know
/The WISC (Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children) is the most widely used individual IQ test in schools. It’s intended to measure the cognitive ability of children ages 6-16 years and 11 months using a variety of subtests.
The test can be administered in paper and pencil format, but you can also now take the WISC test online.
In this article, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about WISC content, WISC scoring, and taking the WISC online.
WISC Basics
The subtests on the WISC are divided into two major types: Performance and Verbal. Students receive an overall IQ score, a Performance IQ, and a Verbal IQ, as well as additional scores designed to indicate relative strengths and weaknesses.
The test generally takes about 65-80 minutes to complete, depending on the amount of subtests you take. Typically, students take either the 10 Primary Scale subtests or 7 Primary-Full Scale IQ subtests.
These subtests are as follows:
As you can see, the various subtests are further divided into skill categories: Verbal Comprehension, Visual Spatial, Fluid Reasoning, Working Memory, and Processing Speed.
No reading or writing is required for the WISC, as the test is designed solely to assess cognitive ability.
WISC Content
On each subtest, questions start out relatively easy and increase in difficulty. Test administrators may end a subtest if they feel that a test-taker has reached the limits of capacity.
In these sections, we’ll explore the questions types you’ll encounter on each WISC subtest.
Similarities
The Similarities subtest is designed to measure logical thinking, verbal concept formation, and verbal abstract reasoning.
Children are provided with two different but similar concepts or objects. They are asked to describe the similarities and differences between the two.
This subtest is untimed.
Vocabulary
On the Vocabulary subtest, students are shown pictures of a word or the word is said aloud. They are expected to provide the name of the object or give a definition for the vocabulary word.
This subtest measures verbal fluency and concept formation, word knowledge, and word usage.
Vocabulary is untimed.
Block Design
The Block Design subtest involves the use of manipulatives. Students are given a set of bi-colored blocks and are asked to arrange them to match a printed image or modeled design.
The goal of this subtest is to assess spatial visualization and analysis, simultaneous processing, visual-motor coordination, dexterity, and nonverbal concept formation, as well as logic and reasoning.
Block Design is a timed subtest, and bonuses are awarded for speed on some of the more difficult designs.
Matrix Reasoning
WISC IV Test Online - Sample Question
Children are shown colorful matrices or other visual patterns with something missing. From a range of options, the student is asked to select the missing piece.
This subtest measures visual processing and abstract, spatial perception. Performance may be influenced by factors such as concentration, attention, and persistence.
This subtest is untimed.
Figure Weights
This Fluid Reasoning subtest measures quantitative reasoning and induction, the ability to make inferences based on provided information.
Students view an image of a scale with missing weight(s) and selects the choice that keeps the scale balanced.
The subtest is untimed.
Digit Span
The Digit Span subtest is divided into two parts. On the first part, the test examiner lists a random string of digits with no relationship to one another. The child must recite the digits in the same order.
On the second part of the text, the examiner again lists a string of random digits. This time, the child must repeat the same digits in reverse order.
These exercises assess the child’s attention and short-term auditory retention, and the test is untimed.
Coding
The Coding subtest evaluates visual-motor dexterity, associative nonverbal learning, and nonverbal short-term memory. Fine-motor dexterity, speed, and accuracy, as well as perceptual organization, are also important.
The Coding test varies slightly according to age.
Children ages 6-7 take a picture-based subtest. At the top of the page is a key containing a set of images, each with a particular mark. Students must mark all other figures on the page to match the key.
For children ages 8-16 the key consists of boxes containing a numeral in the top line and a symbol in the bottom line. They must write the symbol corresponding to each numeral in the worksheet provided.
Coding is a timed subtest.
Visual Puzzles
To answer these questions, students view a completed puzzle. Then, the child selects three response options that reconstruct the provided puzzle.
By completing these puzzles, students demonstrate the ability to analyze and synthesize information.
Visual Puzzles is an untimed subtest.
Picture Span
To demonstrate visual working memory, students view a stimulus page of a picture or pictures for a specified amount of time. Next, students select the picture(s) from options on a response page, preferably in sequential order.
This subtest is also untimed.
Symbol Search
On the Symbol Search subtests, students are presented with a target symbol. The target symbol is not a familiar letter or number, but a geometric form. Students must then determine if the target symbol appears among the symbols included in a provided search group.
This subtest requires perception, recognition, speed, accuracy, attention, and concentration.
Symbol Search is a timed subtest.
Complementary Subtests
On the latest edition of the WISC, the WISC-V, five new complementary subtests have been added. These subtests assess cognitive processes that are linked to academic achievement in reading, math, and writing.
Additionally, these subtests assess processes that have shown sensitivity to a variety of learning disabilities and other clinical conditions.
The five complementary subtests are:
The first two complementary subtests assess naming facility, which refers to rapid automatized naming. The final three are designed to measure visual verbal associative memory.
WISC Test Online
You can take the WISC test online through Q-interactive, an online assessment tool. Q-interactive provides access to the same content that is found on the WISC-V paper and pencil test.
Q-interactive gives you step-by-step help administering the WISC, displaying stimuli, capturing the child’s responses, and scoring. You’re even provided with item-level administration directions.
The WISC test online is scored in real-time, and you’re given immediate access to results and reports.
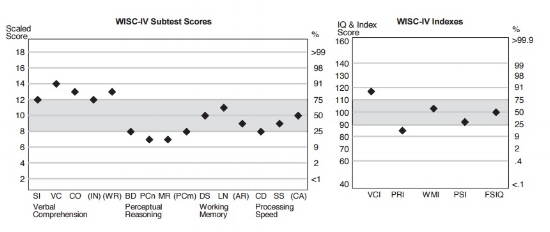
WISC Scoring
WISC Test Online - WISC Score Report Sample
With the ten primary subtests, the WISC-V can provide a Full Scale Intelligence Quotient score (FSIQ), five primary index scores, and three ancillary index scores.
The Full Scale IQ score is derived from the scaled scores a student receives on the subtests. It is considered the most reliable score provided by the WISC and is believed to be an indicator of important life outcomes.
The Primary Index Scales are scores that represent ability in the following areas:
The three Ancillary Index Scales that can be derived from the ten primary subtests are:
These index scores provide a more comprehensive picture of intellectual ability and provide an understanding of a child’s relative strengths and weaknesses.
Can You Prepare for the WISC?
Since it is intended to assess cognitive ability, the WISC is designed to be resistant to preparation.
However, you are likely to perform better on the test if you take the time to become familiar with the unique question types that you will encounter on the WISC.
The more you can build familiarity by viewing or practicing sample questions, the more confident and prepared you’ll be on test day.
You can also read more to improve vocabulary and complete workbooks that involve puzzles, logic, and patterns. Any consistent activity that sharpens and conditions the mind can translate to a better performance on the WISC.
Whether you take a paper-pencil version of the WISC or decide to complete the WISC test online, it’s one of the best and most reliable measurements of cognitive ability in children.